Monday 26 March 2012
Sunday 25 March 2012
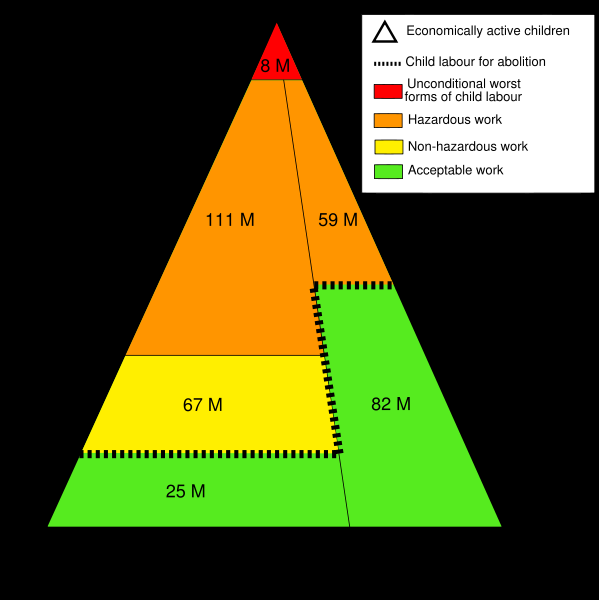
What is Child Labour
Child labour is done by any working child who is under the age specified by law. The word, “work” means full time commercial work to sustain self or add to the family income. Child labour is a hazard to a Child’s mental, physical, social, educational, emotional and spiritual development. Broadly any child who is employed in activities to feed self and family is being subjected to “child labor’.
It is obligatory for all countries to set a minimum age for employment according to the rules of ILO written in Convention 138(C.138). The stipulated age for employment should not be below the age for finishing compulsory schooling, that is not below the age of 15. Developing countries are allowed to set the minimum age at 14 years in accordance with their socio- economic circumstances.
C-138 has also made provisions for flexibility for certain countries, setting the minimum age of 12 and 13 for their children - but only for partaking in light work. Light work can be defined as children’s participation in only those economic activities which do not damage their health and development or interfere with their education. Yes, work that does not obstruct with a child’s education is considered light work and allowed from age 12 under the International Labour Organisation (ILO Convention 138). It is because of this that many children employed in part time work like learning craft or other skills of a hereditary nature are not called child labours. The same work translates into child lab or if a child is thrown into weaving carpets, working into factories or some other employment to earn money to sustain self, or augment his family’s income - without being given school education and allowed opportunities for normal social interactions. A child working part time (3-4 hours) to learn and earn for self and parents after school, is not considered ‘child labor’.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)